Research Interests – Nucleic Acid-Protein Complexes, Gene Expression, Transposons, RNA Splicing and Disease Connections
Current Projects
Biochemistry of P element transposase, the mechanism of transposition and P element-related THAP 9 genes in humans and zebrafish.
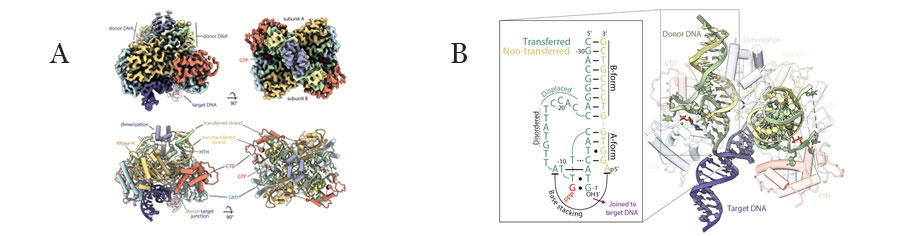
Figure 1. Cryo-EM structural model of the P element strand transfer complex. A) overall structure showing protein and DNA. B) Unusal A-form DNA structure and refolded DNA at the transposon ends. Taken from Ghanim et al. 2019.
RNA binding proteins and the control of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in Drosophila and humans.

Figure 2. P element exonic splicing silencer complex and sequence-specific RNA binding proteins. A) The P element exonic splicing silencer complex (ESS) is assembled containing U1 snRNP and the RNA binding proteins PSI, hrp48, hrp36, hrp38 and PABP-C. Assembly of this complex blocks U1 snRNP binding to the accurate IVS3 5’ splice site. B) The RNA binding proteins PSI and hrp48 bind specifically to the P element ESS. PSI has 4 N-terminal KH-type RNA binding domains and a C-terminal region that interacts with U1-70K protein. hrp48 contains two N-terminal RNP-CS type RNA binding domains and a C-terminal RGG low complexity domain.

